
What is PAM ?
Privileged IDs
A privileged ID is a highly privileged ID that is represented by a Windows Administrator, Linux root, AWS IAM user, or Azure AD Global Administrator. It is used for system operation, system maintenance, and so on. Because privileged IDs are very powerful, they pose a significant security risk if someone using them is malicious or if they are stolen by a malicious person, they must be managed strictly.
Differences between privileged IDs and general user IDs
An example is a Windows Administrator. They temporarily allow the use of a shared ID with full control when needed.
One ID is created for each person when they enter the company and is granted necessary privileges. The ID is deleted when the person leaves the company.
Objectives of privileged access management
The three main objectives of privileged access management are security, compliance, and cost reduction (efficiency).

SECURITY
It supports the prevention of fraud by privileged users and the implementation of measures against cyber attacks, which have become a major threat in recent years.
COMPLIANCE
It supports the enhancement of controls such as internal controls and J-SOX auditing, and the handling of guidelines such as FISC safety standards and PCI DSS.
COST REDUCTION
Workstyle reform and operation outsourcing are attracting attention. iDoperation supports reduced operations in information system departments and outsourcing of management operations.Security
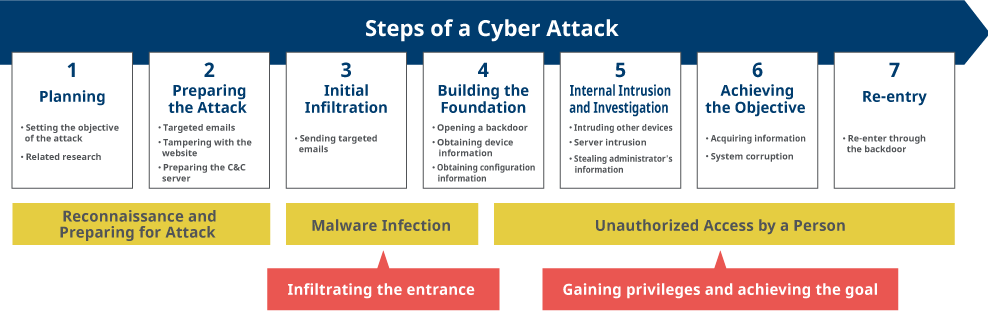
Recently, there have been many incidents related to privileged users, such as internal fraud and cyber attacks.
Internal fraud and cyber attacks often attempt to steal privileged IDs such as roots or Administrators on servers, including authentication servers, because they allow efficient, unauthorized access to a lot of information. When a privileged ID is stolen, that increases the risk of information leaks and other security leaks. For that reason, privileged IDs must be properly managed.
Compliance
It is necessary to properly manage and operate privileged access in order to strengthen controls including internal controls and J-SOX audits, and to respond to various legal guidelines, including the FISC Security Guidelines, PCI DSS, and the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Separation of duties in internal controls is a method of placing restraints in the work flow through measures such as clarifying the jobs and responsibilities of employees and separating authorizers from workers. However, privileged access which have full control are not compatible with separation of duties and require strict control and audits.
Our consultation on auditing trends
- Insufficient application and approval procedures for use of privileged IDs
- Insufficient identification of privileged ID users
- Insufficient monitoring of privileged ID access logs
- Insufficient listing of privileged users (people / privileges)
- Passwords of privileged IDs are not changed regularly
In order to control the use of privilege IDs, it is necessary to clarify who can use them, grant access with only necessary privileges temporarily, and monitor.
In recent years, the progress of the digital transformation has led to a rapid increase in the number of businesses adopting the cloud. Core systems and other important systems that deal with areas such as wages, financial accounting, and human resources that have a direct impact on financial statement audits, are also being transferred to the cloud.
As important systems move to the cloud, it has become necessary to respond to and comply with strict regulations and guidelines concerning the cloud and systems running on it. It is important to grant privileged access—on-premises and on the cloud—only temporarily and with approval, to exercise monitoring (inspecting access and operation logs) in order to establish internal controls.
Cost reduction
Appropriate control of privileged IDs is required in terms of compliance and security.
However, trying to manage privileged ID management without tools requires a lot of administrative work such as changing passwords, listing IDs, and matching access logs against application forms.
As work styles change and more work is being outsourced, there is a need to automate work and reduce the operational workload related to privileged access management.
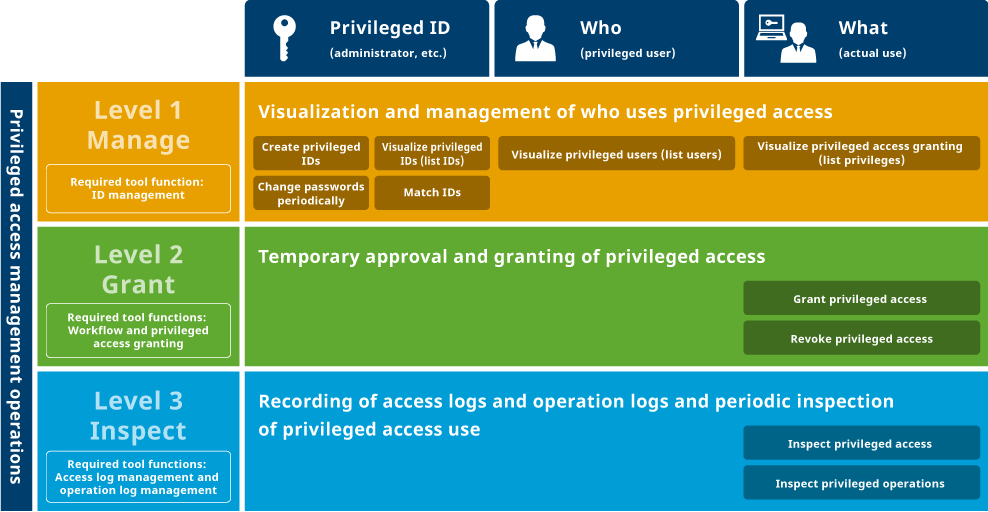
Three operations are required for privileged access management
Various laws and guidelines require proper management of privileged access. Such requirements can be met through three operations: privileged ID management (Level 1), privileged access granting (Level 2) and privileged access inspection (Level 3).
Common issues
- Issues
- Management
-

- Privileged IDs or privileged users are not accurately listed and you don't know who can use privileged IDs.
-

- Password changes or identity matching is not performed in line with predetermined rules.
- Issues
- Granting
-

- The administrator is burdened by many tasks, such as password notification when privileged access is granted, password changes after use, and approval at nighttime or in the event of sudden trouble.
-

- The user cannot be identified or user access cannot be restricted because more than one user shares one privileged ID.
- Issues
- Inspection
-

- There is no way to check when, who, and for what purpose the privileged ID was used.
-

- Matching access logs against application information takes time and effort. Moreover, the operation details of unauthorized privileged access cannot be confirmed.

-
What is iDoperation ?
-
Features